Mesh routers are a modern solution for creating a seamless Wi-Fi network throughout large areas, eliminating dead zones that traditional routers often leave. Unlike single-point routers, which may struggle to provide consistent connectivity in larger homes, mesh routers consist of multiple nodes that work together to extend the network range. This architecture ensures that users experience uninterrupted Wi-Fi coverage, even in multi-floor buildings or homes with complex layouts.
The popularity of mesh systems has grown rapidly, especially as the demand for high-speed internet and reliable Wi-Fi connections increases. According to a 2024 report by Windows Central, mesh routers are a preferred choice for households needing robust, flexible coverage. While mesh systems are often praised for convenience and scalability, there are also potential drawbacks to consider, especially for certain types of users. This article discusses the basics of mesh routers, how they work, and their disadvantages compared to traditional routers.
What Are Mesh Routers?
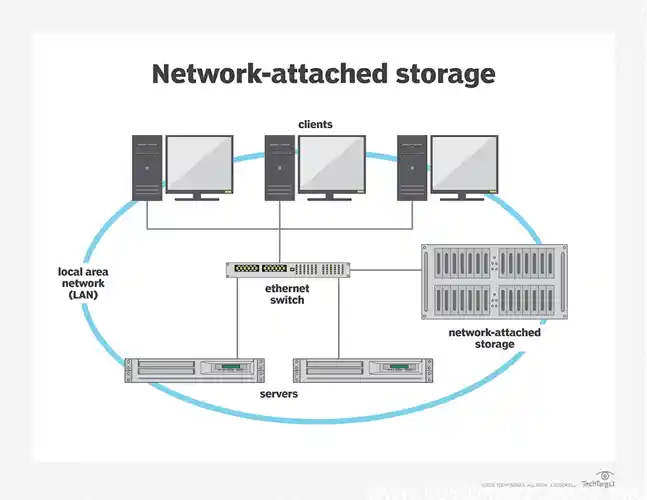
Mesh routers are a type of Wi-Fi network system designed to eliminate dead zones and provide full Wi-Fi coverage throughout a property. Instead of relying on a single router, a mesh system uses multiple nodes placed in various locations within the home. Each node acts as an access point, connecting to each other to create a unified network with one SSID, or network name. This structure allows for continuous coverage, as each node can direct traffic without overloading any single point.
With Mesh Wi-Fi systems, users can connect to the internet seamlessly, even while moving around a property, as the Wi-Fi signal transfers between nodes. The flexibility of mesh networks, which often support both 2.4GHz and 5GHz bands, makes them ideal for larger spaces. However, mesh systems can be more costly than traditional routers, and some users may find setup and maintenance more complex, especially when additional features or compatibility issues arise.
How Mesh Routers Work Compared to Traditional Routers
Mesh routers differ significantly from traditional routers in terms of both structure and performance. While a traditional router relies on a single device to broadcast Wi-Fi throughout an area, mesh systems use multiple nodes that communicate with each other to form a Mesh Wi-Fi network. This network type enables consistent coverage across multiple rooms or floors, reducing the likelihood of dead zones and weak spots.
For example, if a user moves from one room to another, a mesh system automatically transitions their connection from one node to another without interrupting the Wi-Fi signal. In contrast, traditional routers often require Wi-Fi extenders to increase coverage, but these extenders can create issues with speed and consistency. According to research from Esploro Research and Profolus, mesh networks offer a smoother Wi-Fi experience, but they also come with higher setup costs and may require advanced setup knowledge.
Key Disadvantages of Mesh Routers
Despite their advantages in coverage, mesh routers come with several potential drawbacks that may make them less suitable for certain users. One significant disadvantage is the higher cost compared to traditional routers, with mesh systems often priced substantially higher due to the multiple nodes required. Additionally, setting up a mesh network can be more complex, requiring a good understanding of network configurations. Users should also consider potential signal strength loss when adding multiple nodes, as this can impact performance. Furthermore, older devices may face compatibility issues with some mesh networks, particularly if the device is not updated to support newer Wi-Fi standards.
Higher Cost Compared to Traditional Routers
Mesh routers typically have a higher price point than traditional routers due to the need for multiple nodes to create a robust network. A basic mesh system can range from $200 to $500 or more, while a traditional router usually costs around $100 to $200. For users with larger homes requiring strong, uninterrupted Wi-Fi coverage, the investment might be worthwhile. However, for smaller spaces or single-story homes, the cost of a mesh system may not offer a proportionate benefit. Additionally, some mesh systems charge an annual subscription fee for advanced features, adding to the overall cost. According to a 2024 Profolus report, many consumers prefer traditional routers due to this pricing disparity.
Complexity in Initial Setup
Is Setting Up a Mesh Router Difficult?
Yes, setting up a mesh router can be challenging, particularly for users unfamiliar with Wi-Fi configurations. Unlike traditional routers, which are generally plug-and-play, mesh systems require precise placement of each node to maximize signal coverage and avoid interference. Initial setup may involve configuring each node individually, syncing SSIDs, and managing band selection (such as 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz). Some systems also require specific mobile applications or web interfaces for setup, which may not be intuitive. According to Esploro Research, users new to networking often report difficulty with these setups, although support options are generally available to assist.
Potential Signal Loss with More Nodes
Adding multiple nodes in a mesh network can sometimes lead to signal strength loss, particularly if nodes are placed too far apart or in areas with physical obstructions. Factors like walls, metal surfaces, and even certain electronic devices can interfere with Wi-Fi signal transmission between nodes. According to studies by Profolus in 2022, placing nodes within optimal distances (usually between 10–15 feet) minimizes signal degradation. However, if too many nodes are used, network congestion can occur, reducing internet speed across the network. Regular firmware updates and proper node placement can help to mitigate these issues, but users should be aware of potential performance impacts with extensive mesh setups.
Limited Compatibility with Some Devices
Older devices or those not updated to support current Wi-Fi standards may experience compatibility issues with mesh routers. Many mesh systems operate primarily on 5 GHz or 6 GHz bands, which may not be supported by devices that are only compatible with 2.4 GHz. This issue can cause connectivity problems, reduced speed, or even an inability to join the network. Windows Central notes that compatibility issues are common with older smart home devices and appliances, which rely on the 2.4 GHz band. Users should check device compatibility before upgrading to a mesh system, especially if they rely on devices with outdated connectivity specifications.
Cost Analysis of Mesh Routers
Mesh routers are increasingly popular for their ability to provide broad Wi-Fi coverage, but this functionality comes at a higher price. This section explores whether mesh routers are more costly than traditional routers and evaluates if the expense is justified for home users. By comparing costs and the benefits of both mesh Wi-Fi and traditional routers, users can make an informed choice based on budget and coverage needs. Several factors, including the number of nodes, setup fees, and optional subscription services for enhanced features, all influence the total cost of owning a mesh system.
Are Mesh Routers More Expensive Than Traditional Routers?
Yes, mesh routers are generally more expensive than traditional routers due to the multi-node design and advanced technology required for seamless Wi-Fi coverage. The typical cost of a basic mesh system with two or three nodes can range from $200 to $500 or more, whereas a single traditional router usually costs between $100 and $200. According to a 2024 report from Windows Central, consumers often pay a premium for mesh systems due to the convenience of unified coverage and fewer dead zones.
While mesh systems provide comprehensive Wi-Fi coverage ideal for larger or multi-story homes, they might not be the best investment for smaller properties. Additionally, certain mesh providers charge an annual subscription fee for features like enhanced security or parental controls, further raising the cost. For users on a budget, traditional routers may offer adequate coverage at a lower price point.
Is a Mesh Router Worth the Cost for Home Users?
Whether a mesh router is worth the cost depends on the home’s size, layout, and Wi-Fi needs. Mesh systems are ideal for larger homes or properties with multiple floors where traditional routers may struggle to provide consistent coverage. The multiple nodes in a mesh network work together to eliminate dead zones and maintain a strong Wi-Fi signal throughout the space, making them valuable for families with high connectivity demands.
However, in smaller homes or apartments where a single router can provide adequate coverage, the cost of a mesh system may not be justified. For example, homes under 2,000 square feet often see minimal benefit from mesh Wi-Fi compared to a high-quality traditional router. According to Profolus, users should weigh the need for seamless connectivity and coverage against the higher cost to determine if a mesh network is the best choice for their home.
Common Issues Faced with Mesh Routers
Mesh routers provide broad Wi-Fi coverage and seamless connectivity across large areas, but they also come with certain drawbacks. Common issues include coverage overlaps, channel interference, and the need for regular updates and maintenance. Understanding these disadvantages can help users decide if a mesh Wi-Fi network is the right fit for their needs or if a traditional router might be a more suitable option.
Coverage Overlaps and Channel Interference
Coverage overlaps and channel interference are notable issues with mesh Wi-Fi networks. In areas where multiple nodes are installed close to each other, their overlapping coverage zones can lead to signal congestion and interference. This is especially problematic in high-density residential areas, where neighbors may have Wi-Fi networks operating on the same channels, typically 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz.
To mitigate this issue, some mesh routers allow users to manually adjust channel settings or rely on automatic channel-switching to avoid interference. However, even with these features, some interference may persist, impacting network speed and reliability. According to Esploro Research, channel interference is one of the most common complaints among users of mesh Wi-Fi systems, as it can degrade the network’s overall performance, particularly during peak usage hours.
Need for Regular Updates and Maintenance
Mesh routers require regular firmware updates and maintenance to function optimally, which can be a drawback for users looking for a low-maintenance solution. These updates, often necessary to address security vulnerabilities and improve network stability, are sometimes complex and time-consuming. Some mesh systems update automatically, but others require manual action by the user.
Additionally, firmware updates may occasionally lead to compatibility issues with certain devices, necessitating further troubleshooting. Windows Central highlights that missing or skipping updates can lead to performance degradation, as the router may lack the latest optimizations for speed and security. For households or businesses where mesh Wi-Fi is critical, staying on top of updates is essential to maintain a secure, stable network, though it may add to the operational workload.
Comparing Mesh Routers with Traditional Routers
Mesh routers and traditional routers offer distinct approaches to Wi-Fi coverage. Understanding their differences can help users decide which option best meets their connectivity needs and space requirements. While traditional routers are often more affordable and straightforward, mesh routers excel in providing expansive coverage, especially in larger areas with multiple rooms and obstructions.
Differences in Coverage and Performance
Coverage and performance are critical factors differentiating mesh routers from traditional routers. A traditional router typically emits Wi-Fi from a single point, which can limit its reach, particularly in large homes or offices. In contrast, a mesh system uses multiple nodes to blanket the area in consistent Wi-Fi coverage. Each node communicates with others to eliminate dead zones, making mesh Wi-Fi ideal for environments with obstructions such as walls and floors.
However, despite the improved range, mesh systems may experience signal degradation when many nodes are added. According to Windows Central, each additional node can introduce potential latency, impacting overall performance slightly more than with a high-powered traditional router. Mesh routers can offer superior coverage but may not always match the peak speed and stability of a single high-performance router.
Pros and Cons of Mesh Routers vs. Single Traditional Routers
Choosing between a mesh router and a traditional router involves weighing their respective advantages and disadvantages. Mesh routers provide seamless, expansive Wi-Fi coverage, ideal for eliminating dead zones in large homes. They also offer self-healing networks; if one node fails, others maintain the connection. However, mesh systems are often more expensive, with individual nodes increasing the cost compared to a single traditional router.
In contrast, traditional routers are generally more affordable and simpler to set up. They often provide high-speed connectivity in a concentrated area, making them suitable for smaller spaces. According to Esploro Research, traditional routers may be a better option for users who prioritize speed over coverage area. However, they lack the adaptability of mesh systems and may require range extenders for full coverage, which can add to costs and complicate the network setup.
How to Mitigate Mesh Router Disadvantages
While mesh routers offer improved Wi-Fi coverage across large spaces, users can face certain challenges, such as signal loss, higher costs, and setup complexity. However, these disadvantages can be minimized with strategic node placement and the correct choice of mesh Wi-Fi system for your space. By optimizing node positions and understanding the requirements of the area, users can ensure maximum Wi-Fi efficiency and reliability.
Choosing the Right Number of Nodes for Your Space
Choosing the optimal number of nodes is essential to prevent performance issues in mesh Wi-Fi systems. Each additional node expands coverage, but an excessive number can cause signal interference or unnecessary costs. For example, Windows Central suggests using three nodes for average homes and increasing to five nodes for larger properties with multiple floors. Generally, a node should be placed within 30 feet of the next one, ensuring consistent coverage and limiting potential Wi-Fi drops.
By assessing the space requirements, users can avoid purchasing extra nodes they may not need. Rooms with thicker walls or multiple obstructions may require more nodes for stability, while open areas may need fewer. Choosing the right number ensures efficient mesh Wi-Fi operation, reducing costs and optimizing Wi-Fi performance.
Optimizing the Placement of Mesh Nodes
Node placement plays a crucial role in the performance of a mesh Wi-Fi network. Poor placement can lead to weak signals, interference, and Wi-Fi drops. For effective setup, place each node in a central position relative to its coverage area, ideally at an elevated height. Avoid areas with dense obstacles like walls or metal objects, which can obstruct Wi-Fi signals. Positioning nodes closer to 2.4GHz and 5GHz access points can improve SSID strength and reduce signal interference.
Optimal node placement helps maintain the mesh network’s stability. Each node should be spaced evenly to form a continuous, reliable connection. According to Esploro Research, an organized layout where nodes create an overlapping coverage zone can prevent dead spots. This approach ensures users get the most out of their mesh Wi-Fi system with minimal interference or signal degradation.
FAQ’s
1. Can mesh routers be used with traditional routers?
Yes, mesh routers can work alongside traditional routers by connecting one node to the existing router, creating a mesh network that extends Wi-Fi coverage.
2. Do mesh routers automatically update their firmware?
Many mesh routers have auto-update features, but not all. Regular updates are essential to improve performance and security, so check for automatic update options in the settings.
3. Are mesh routers ideal for small homes or apartments?
In smaller spaces, a single traditional router may be more cost-effective. Mesh routers benefit larger areas where extended Wi-Fi coverage is needed.
4. Will adding more nodes always improve Wi-Fi speed?
Not necessarily. Adding excessive nodes can lead to signal interference and slower speeds. It’s essential to add the right number based on the coverage area.
5. Do mesh networks work with older devices?
Most mesh Wi-Fi systems support backward compatibility with older devices, but some may face compatibility issues, especially with devices that don’t support modern Wi-Fi standards.