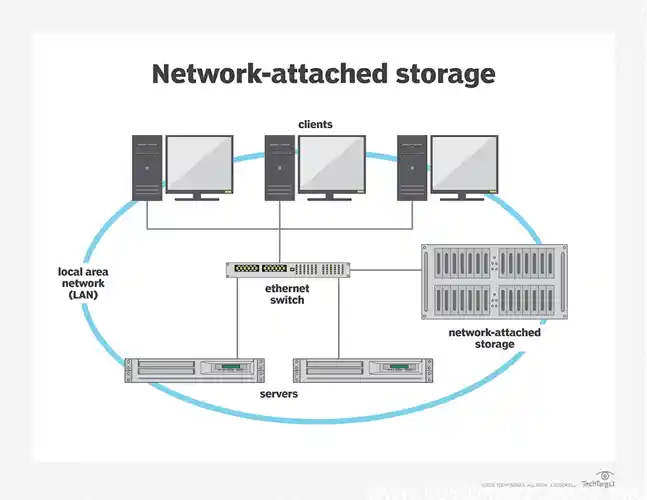
WiFi extenders are devices that expand the coverage of an existing WiFi network by retransmitting its signal to areas where coverage is weak or non-existent. This can help address dead zones in larger homes or areas with multiple walls and obstacles. According to Speedtest.net, homes over 1,500 square feet or with multiple floors often experience WiFi dead spots, which a WiFi extender can mitigate. Extenders are different from WiFi boosters or mesh Wi-Fi systems as they only repeat the existing signal rather than creating a new network. By extending the reach of the WiFi, they provide a more reliable connection for devices across a larger area.
What Is a WiFi Extender?
A WiFi extender is a device designed to improve the reach of a WiFi network. It captures the existing WiFi signal from your router and retransmits it, effectively expanding the coverage range. Unlike mesh Wi-Fi networks, which create an interconnected network of multiple nodes, WiFi extenders serve as simple signal repeaters. They’re often used in buildings with thick walls or larger areas where the primary WiFi router signal doesn’t reach, helping ensure connectivity throughout spaces as large as 5,800 square feet.
How Does a WiFi Extender Work?
WiFi extenders function by capturing the signal from your main WiFi router and amplifying it to reach a greater distance. This process, called signal repetition, helps cover areas previously experiencing low or no connectivity. Once installed and connected to the main router, a WiFi extender retransmits the signal on either the 2.4GHz or 5.0GHz frequency band, creating a reliable connection across larger spaces. For instance, a Netgear Nighthawk AX8 extender can effectively increase signal range across multiple rooms, ensuring smooth internet access for all connected devices.
Do WiFi Extenders Really Work?
WiFi extenders are effective tools to improve coverage in areas where the main router’s WiFi signal does not reach. They work by capturing the existing WiFi from the router and retransmitting it to areas with weak or no signal, often extending coverage by 250 to 1,500 square feet. They are commonly used in large or multi-story homes, where obstacles like walls can interrupt the WiFi signal. According to Consumer Reports, extenders like the Netgear Nighthawk AX8 have shown to help reduce buffering and improve internet speed in dead zones, especially when positioned at the edge of the router’s effective range. Extenders are ideal for general tasks such as streaming and web browsing but may not match the speed or seamless connectivity offered by a mesh Wi-Fi network.
How Effective Are WiFi Extenders for Improving Coverage?
WiFi extenders significantly improve coverage by expanding the signal range of an existing network, making them especially useful in homes over 1,500 square feet or with multiple walls between the router and devices. Tests from Speedtest.net show that top-performing extenders can boost signal coverage up to 100% in previously low-connectivity areas. However, their effectiveness depends on the strength of the original signal and proper placement—ideally halfway between the router and the dead zone. Models like the TP-Link RE315 and Nighthawk AX8 have demonstrated effective WiFi range extension up to 5,800 square feet. This makes them suitable for common household devices, though high-speed tasks may still benefit more from a Mesh Wi-Fi system or Ethernet connection.
Factors Affecting Performance
Several factors impact the performance of WiFi extenders. The quality of the initial WiFi signal, distance from the router, and interference from devices or walls all play crucial roles. Higher-frequency bands, like 5GHz, provide faster speeds but have shorter ranges compared to 2.4GHz bands, which are better at penetrating walls. Extender models like the TP-Link RE315 are designed to operate on both 2.4GHz and 5GHz frequencies, allowing for versatile placement. For optimal performance, experts suggest positioning the extender halfway between the router and the desired coverage area, ideally with minimal obstacles. Ethernet ports on some extenders, such as the Netgear Nighthawk AX8, can also boost connection stability and reduce latency.
When to Use a WiFi Extender
WiFi extenders are best used in situations where specific rooms or areas in a home suffer from poor connectivity, such as a basement, garage, or distant bedrooms. If the main WiFi router is located in one corner of the home, an extender can be placed strategically to fill coverage gaps. In homes larger than 1,500 square feet or multi-level spaces, extenders help improve connectivity without requiring a more complex mesh Wi-Fi system. However, in cases where seamless roaming between rooms is needed, or for homes with high internet demands, a Mesh network might be more efficient.
Best Scenarios for WiFi Extender Use
WiFi extenders are particularly useful in several scenarios. For example, they can be ideal in rental properties where upgrading the existing router is not possible. They also work well in home offices that need a reliable connection for video conferencing but are too far from the primary router. Another scenario involves homes with thick walls or metal appliances that block signals, where an extender helps maintain connectivity throughout the building. According to CNET, users in smaller homes with limited dead zones might find an affordable extender such as one priced under $50 sufficient for daily needs.
Benefits of Using WiFi Extenders
Using WiFi extenders can enhance connectivity throughout your home, particularly in areas where your router’s signal struggles to reach. By extending coverage, they reduce dead zones and provide a smoother online experience for all devices. For homes with larger layouts or obstructive barriers like walls, WiFi extenders can effectively distribute signals to every corner, making online gaming, streaming, and browsing more reliable. Many extenders, such as TP-Link RE315 and Netgear Nighthawk AX8, offer dual-band support, broadcasting on both 2.4GHz and 5GHz frequencies to enhance connection quality. When properly positioned, extenders help reduce lag and improve stability, making them a valuable addition to any home network setup without the need for costly upgrades or replacements.
Improved Signal Strength and Coverage
WiFi extenders significantly enhance signal strength and expand WiFi coverage in spaces with weak or interrupted signals. Positioned between the router and target area, they capture and rebroadcast the signal, making it possible to use the internet in rooms where the connection was previously unreliable. According to Consumer Reports, high-quality extenders like Nighthawk AX8 and RE7310 extend signals up to 5,800 square feet, providing stable connectivity across large spaces. This solution is particularly helpful for maintaining consistent streaming, video calls, and general browsing throughout the home. However, it’s crucial to ensure proper placement of the extender to avoid obstacles and maximize coverage.
Cost-Effective Solution for Coverage Gaps
WiFi extenders offer a cost-effective solution to fill coverage gaps, with entry-level models available for as little as $20. Compared to upgrading to a mesh Wi-Fi network or purchasing a high-end router, a WiFi extender is an affordable way to enhance WiFi coverage in small dead zones. The TP-Link RE315, priced under $30 on Amazon, provides reliable signal extension for light internet tasks, making it a budget-friendly option for most households. Many extenders support dual-band frequencies, allowing users to enjoy better performance without significant costs. They are an ideal choice for renters or anyone seeking quick coverage improvement without permanent installations.
Easy Setup Compared to Other Solutions
Setting up a WiFi extender is typically straightforward, making it accessible even to users with minimal technical knowledge. Most modern extenders feature WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup) buttons for quick pairing with the existing router, eliminating the need for complex configurations. Advanced models, such as TP-Link’s Tether and Netgear’s Nighthawk AX8, come with dedicated apps that guide users through setup in just a few steps. Additionally, Amazon offers a variety of extenders with plug-and-play functionality, allowing for quick installation directly into a wall socket. This simplicity in setup makes WiFi extenders a convenient solution for improving connectivity without the need for professional installation or specialized equipment.
Drawbacks and Limitations of WiFi Extenders
WiFi extenders can effectively expand coverage in homes with spotty Wi-Fi signals, but they come with several limitations. A primary drawback is that they often reduce bandwidth, impacting internet speed. Extenders work by repeating the signal from the router, which can lead to latency, especially if used for data-heavy activities like video streaming or online gaming. Additionally, they may not be compatible with certain devices or networks, especially older models without dual-band support. In large spaces or homes with multiple floors, extenders may only partially solve the problem, leading to incomplete coverage. For larger properties, Mesh Wi-Fi Network Systems or multiple extenders are more suitable, though they come at a higher cost and may require technical setup.
Potential for Signal Loss and Latency Issues
One common limitation of WiFi extenders is their potential to cause signal loss and latency. By extending the router’s Wi-Fi signal, extenders split available bandwidth, which can slow down speeds. Users may experience reduced performance on high-bandwidth applications, such as HD streaming or gaming, due to this limitation. Some extenders, like the Nighthawk AX8, mitigate these issues by supporting both 2.4GHz and 5GHz frequencies, which improves overall data handling. However, latency and lag can still occur, especially in environments with heavy internet use. For critical applications requiring fast speeds, a Mesh Wi-Fi Network System may be a better, though more costly, solution.
Compatibility Issues with Some Devices
Compatibility issues can arise with WiFi extenders, especially for older devices that may not support dual-band connections or advanced configurations. While many modern extenders, like TP-Link’s RE315 and Netgear’s Nighthawk AX8, support compatibility with most ISPs and routers, some devices may experience difficulty connecting, especially those restricted to a single frequency. Users may also face challenges if their devices frequently switch between the extender’s signal and the router, leading to connectivity drops. Dual-band extenders can help address some compatibility issues, but users with mixed device types may need to adjust settings or consider upgrading devices to newer, more compatible options.
Limited Effectiveness for Large Homes or Buildings
For large homes or multi-story buildings, WiFi extenders often provide only partial solutions. Although models like the Netgear Nighthawk AX8 claim to cover up to 5,800 square feet, in practice, walls and floors can still interrupt signals. Large homes may require multiple extenders or an upgrade to a Mesh Wi-Fi system, which provides seamless, integrated coverage throughout the property. In buildings with multiple devices and areas requiring strong connections, extenders alone may not fully address the need. Mesh systems can be more effective for consistent coverage but come at a higher price and involve more complex setup compared to a single extender solution.
Choosing the Right WiFi Extender
Choosing the right WiFi extender requires understanding your specific needs and the extenders’ capabilities. Key factors include the coverage area, speed requirements, and device compatibility with existing networks. Modern extenders, like the Netgear Nighthawk AX8 and TP-Link RE315, provide enhanced range and dual-band support for smoother performance. The WiFi 6 and 6E standards in newer extenders also offer faster speeds and improved device handling, beneficial for busy households. For smaller spaces, a basic extender may suffice, while large homes often benefit from Mesh Wi-Fi Network Systems that ensure seamless coverage across multiple floors. When buying, consider whether the extender supports 2.4GHz and 5GHz frequencies, especially if you have a mixed network environment.
Factors to Consider When Buying a WiFi Extender
When choosing a WiFi extender, several factors are crucial. First, assess your coverage area to determine if a standard extender is adequate or if a Mesh Wi-Fi System may be better suited for larger properties. Speed capacity is another key consideration; high-speed requirements for activities like video streaming or online gaming may require extenders with dual-band support, such as TP-Link’s RE315 or the Nighthawk AX8. Device compatibility is also essential; some extenders are more compatible with specific routers or devices. Lastly, ensure the extender includes easy setup options like WPS to simplify the installation process.
Coverage Area, Speed, and Device Compatibility
Coverage area, speed, and device compatibility are critical when selecting a WiFi extender. The coverage area should match the size of your home; for instance, models like the Netgear Nighthawk AX8 can cover up to 5,800 square feet. However, signal loss may still occur in large, multi-story homes due to obstacles or distance from the router. Speed capability is vital for ensuring that high-bandwidth activities, such as streaming and gaming, are uninterrupted; consider an extender with dual-band support to handle these demands. Additionally, ensure the extender is compatible with your current router and connected devices, particularly if they support 2.4GHz and 5GHz frequencies, as this can impact performance.
Popular WiFi Extender Brands and Models
Top WiFi extender brands include Netgear, TP-Link, and Linksys, known for their robust performance and innovative features. Netgear’s Nighthawk AX8 offers advanced WiFi 6 support, covering large areas with reliable dual-band functionality, ideal for streaming-heavy households. TP-Link’s RE315 is popular for smaller spaces, combining cost-effectiveness with good dual-band coverage. Linksys models, like the RE7310, provide a balance of affordability and performance, supporting 5GHz frequency for minimal lag. These brands consistently receive high ratings from sites like TechRadar and Consumer Reports, making them reliable choices for improving home internet performance.
Comparison with Other Network Solutions
Comparing WiFi extenders with other solutions, such as Mesh Wi-Fi Network Systems and routers with boosters, highlights the strengths and limitations of each. Mesh systems, like the Netgear Orbi or TP-Link Deco, create a unified network that covers large areas without signal drops, making them ideal for multi-story homes. In contrast, WiFi extenders are generally more affordable and easier to install, but may cause speed reduction due to bandwidth splitting. Routers with built-in boosters provide a middle-ground solution, offering slightly extended range without significant speed loss. However, for users seeking seamless coverage and optimal performance, mesh networks tend to outperform traditional extenders.
Tips for Optimizing WiFi Extender Performance
Optimizing the performance of your WiFi extender ensures maximum coverage and reliable connectivity throughout your home. Start by selecting a high-quality extender from reputable brands like Netgear or TP-Link, which offer models such as the Nighthawk AX8 and RE315 known for their robust performance. Position the extender strategically—ideally halfway between your router and the area with weak signal—to effectively amplify the WiFi signal. Regularly update the extender’s firmware through apps like TP-Link’s Tether to benefit from the latest performance enhancements and security features. Additionally, minimize interference by placing the extender away from electronic devices that operate on 2.4GHz or 5GHz frequencies, such as Bluetooth speakers or microwaves. By following these tips, you can significantly improve your extender’s efficiency, ensuring a stable and fast internet connection across your entire living space.
Ideal Placement for Maximum Coverage
Ideal placement of your WiFi extender is crucial for achieving maximum coverage and optimal performance. According to Consumer Reports, the best location is approximately halfway between your router and the area where the signal is weak. This positioning allows the extender to receive a strong signal from the router and effectively rebroadcast it to the desired area. Avoid placing the extender near large metal objects or electronic devices that can cause interference, such as microwaves or Bluetooth speakers. Additionally, elevating the extender on a shelf rather than placing it on the floor can enhance signal distribution. For larger homes, consider using multiple extenders from brands like Netgear or TP-Link to ensure comprehensive coverage. Proper placement not only maximizes the extender’s efficiency but also minimizes signal loss and latency, providing a seamless internet experience throughout your home.
Ensuring Compatibility with Your Router
Ensuring compatibility between your WiFi extender and router is essential for seamless performance. Verify that both devices support the same WiFi standards, such as WiFi 5 (802.11ac) or WiFi 6 (802.11ax), to ensure optimal speed and connectivity. Brands like Netgear and TP-Link offer extenders that are specifically designed to work with their own routers, such as the Netgear Nighthawk AX8 extender with Netgear routers. Additionally, check for dual-band support (2.4GHz and 5GHz) to maintain high-speed connections across different devices. Utilizing features like WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup) can simplify the pairing process between your extender and router, reducing the chances of compatibility issues. By selecting a compatible extender, you ensure a stable and efficient network, enhancing your overall internet experience without the need for extensive technical adjustments.
Troubleshooting Common Issues with WiFi Extenders
Troubleshooting common issues with WiFi extenders can help maintain a stable and efficient network. One frequent problem is signal loss, which can be mitigated by repositioning the extender to a more optimal location, ideally halfway between the router and the affected area. Latency issues or lag during high-bandwidth activities like video streaming or online gaming can often be resolved by switching to a less congested 5GHz frequency band, supported by extenders such as the TP-Link RE315 or Netgear Nighthawk AX8.
If compatibility issues arise, ensure that both the extender and router are updated with the latest firmware from their respective manufacturers, accessible via apps like TP-Link’s Tether or Netgear’s Genie. Additionally, resetting the extender to factory settings can resolve persistent connectivity problems. For persistent issues, consulting resources from Consumer Reports or reaching out to customer support from brands like Netgear or TP-Link can provide further assistance. Effective troubleshooting ensures your WiFi extender continues to deliver reliable and high-performance connectivity.
FAQ’s
1. Do WiFi extenders actually improve internet speed?
Answer: WiFi extenders don’t increase your internet speed from your ISP, but they enhance signal strength and extend coverage, allowing for better connectivity in weak-signal areas.
2. Where should I place my WiFi extender for best results?
Answer: Position it halfway between your router and the area with a weak signal. Avoid placing it near metal objects or other electronics that could cause interference.
3. Can a WiFi extender work with any router?
Answer: Most extenders are compatible with any router, but check for matching WiFi standards (e.g., WiFi 5 or WiFi 6) and dual-band capability for optimal performance.
4. How many WiFi extenders can I use in my home?
Answer: Using more than two extenders may cause signal interference. For large homes, consider a mesh network instead for consistent, widespread coverage.
5. Why is my WiFi extender slowing down my internet connection?
Answer: Extenders may reduce speed due to signal loss and latency. Try moving the extender closer to the router or using the 5GHz band for faster data transmission.